How to manually operate a solenoid valve?
Understanding Solenoid Valves
Solenoid valves play a crucial role in various applications, including agriculture, where they are essential for crop spraying systems. To make informed decisions, it’s important to understand the basics of solenoid valve operation and the different types available.
Basics of Solenoid Valve Operation
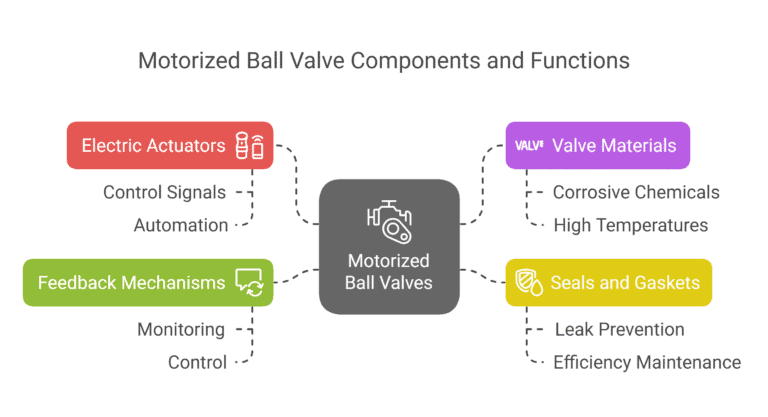
A solenoid valve controls the flow of liquids or gases using an electromagnetic solenoid. When the solenoid is energized, it creates a magnetic field that moves a plunger or piston, opening or closing the valve. For a 2 way solenoid valve, there are two pipe connections: an inlet (cavity port) and an outlet (body orifice port). When the valve is energized, the plunger opens, allowing media to flow from the cavity port to the body orifice port. When the power is turned off, the orifice closes, stopping the flow (Solenoid).
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Inlet Port | Cavity port where the media enters |
| Outlet Port | Body orifice port where the media exits |
| Operation | Electromagnetic solenoid controls plunger movement |
| Function | Controls the flow of liquids or gases |
For more details on how a 2 way control valve works, visit our article on how does a 2 way control valve work.
Types of Solenoid Valves
There are several types of solenoid valves, each designed for specific applications. The main types include:
- 2-Way Solenoid Valves: These have one inlet and one outlet and are used to allow or shut off the flow of media. They are available in either normally open or normally closed configurations.
- 3-Way Solenoid Valves: These have three ports and can direct flow between two outlet ports, commonly used for diverting media.
- 4/2-Way Solenoid Valves: These have four ports and two positions, typically used to control double-acting cylinders in pneumatic systems.
- 5/2-Way Solenoid Valves: These have five ports and two positions, designed for controlling the airflow to and from pneumatic actuators.
| Type | Ports | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2-Way | 2 | One inlet, one outlet, used for on/off control |
| 3-Way | 3 | Directs flow between two outlets |
| 4/2-Way | 4 | Controls double-acting cylinders |
| 5/2-Way | 5 | Controls airflow for pneumatic actuators |
Selecting the right type of solenoid valve depends on the specific requirements of your application. For more information on the differences between 2 way and 3 way solenoid valves, check out what is the difference between a 2 way and 3 way solenoid valve?.
Applications of 2-Way Solenoid Valves
Understanding the applications of 2-way solenoid valves is essential for their effective use. These valves have two pipe connections – an inlet and an outlet – and are used to control the flow of liquids or gases, allowing or stopping the flow as needed. Let’s explore their use in industrial and agricultural settings.
Industrial Use Cases
In industrial environments, 2-way solenoid valves play a critical role in various applications. They are commonly used to control the flow of liquids and gases such as water, air, gas, and oil. These valves can be found in a range of industries including manufacturing, automotive, and chemical processing. Here are some examples:
- Manufacturing: In automated systems, these valves are used to control the flow of lubricants, coolants, and compressed air, ensuring smooth operation of machinery.
- Automotive: Solenoid valves manage fuel injection systems, controlling the flow of gasoline or diesel to the engine’s combustion chambers.
- Chemical Processing: These valves regulate the flow of chemicals in processes like mixing, heating, and cooling, ensuring precise control and safety.
| Industry | Application | Medium Controlled |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Lubricants, Coolants, Compressed Air | Oil, Water, Air |
| Automotive | Fuel Injection Systems | Gasoline, Diesel |
| Chemical | Chemical Mixing, Heating, Cooling | Chemicals, Water |
For more details on how these valves operate, visit how does a 2 way control valve work.
Agricultural Implementations
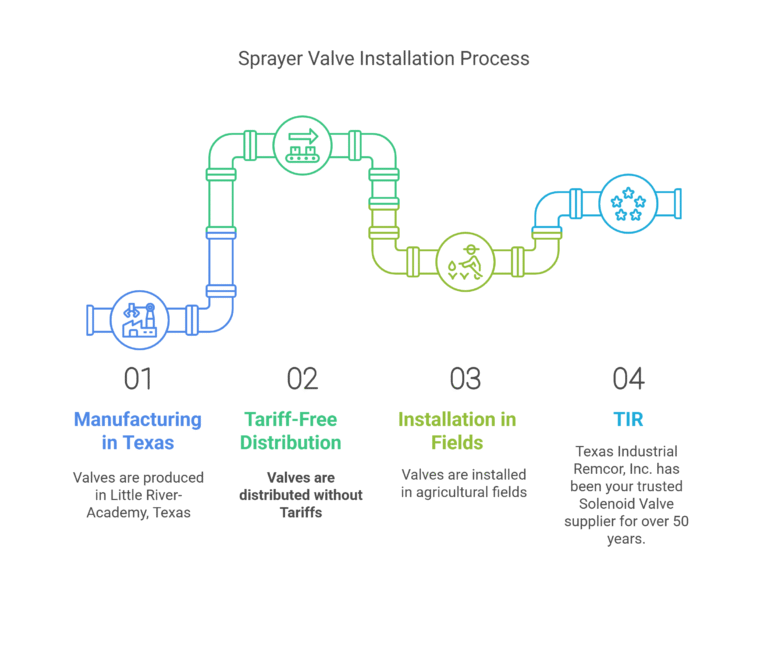
In the agricultural sector, 2-way solenoid valves are essential for various irrigation and crop spraying systems. These valves ensure precise control over the flow of water and fertilizers, optimizing crop yield and conserving resources. Here are some key applications:
- Irrigation Systems: Solenoid valves control the flow of water to different sections of a field, allowing for automated and efficient irrigation.
- Crop Spraying: These valves manage the distribution of fertilizers and pesticides, ensuring even coverage and reducing waste.
- Greenhouse Climate Control: Solenoid valves regulate the flow of water and nutrients in hydroponic systems, maintaining optimal growing conditions.
| Application | Description | Medium Controlled |
|---|---|---|
| Irrigation Systems | Automated control of water flow | Water |
| Crop Spraying | Distribution of fertilizers and pesticides | Fertilizers, Pesticides |
| Greenhouse Control | Regulation of water and nutrients in hydroponics | Water, Nutrients |
For more information on selecting the right valve for agricultural use, see our guide on 2 way solenoid valve.
By understanding the diverse applications of 2-way solenoid valves in both industrial and agricultural settings, you can make informed decisions about their use in your operations. Whether you need to manage the flow of water in irrigation systems or control lubricants in manufacturing, these valves offer reliable and efficient solutions. For further insights, check out what is the difference between a 2 way and 3 way solenoid valve?.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Solenoid Valves
When selecting the right 2 way solenoid valve for your agricultural needs, there are several factors to keep in mind. These factors will ensure the valve operates efficiently and lasts longer.
Material Selection
Solenoid valves are made from a variety of materials, each with its own properties to resist different environmental and chemical conditions. The choice of material is crucial when dealing with different media such as water, air, or chemicals.
| Material | Suitable For | Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Plastic | Water, low-pressure applications | Corrosion-resistant, lightweight |
| Brass | Neutral liquids and gases | Durable, cost-effective |
| Stainless Steel | Aggressive chemicals, food and beverages | High corrosion resistance, safe for human consumption |
| Aluminum | Air, non-corrosive liquids | Lightweight, good heat dissipation |
When choosing a material, consider the chemical composition, temperature, and pressure of the media. For example, stainless steel valves are ideal for applications involving human consumption due to their high resistance to corrosion and compliance with safety standards.
For more in-depth information on materials, you can refer to our guide on how does a 2 way control valve work.
Environment and Safety Factors
The environment in which the solenoid valve will be used plays a significant role in its selection. Factors to consider include exposure to harsh outdoor conditions, corrosive substances, explosive or dusty environments, and moisture levels.
- Outdoor Conditions: If the valve will be exposed to harsh outdoor conditions, select materials that can withstand temperature variations and UV exposure.
- Corrosive Environments: For environments with corrosive substances, materials like stainless steel or specific plastics are preferable.
- Explosive Environments: In explosive or dusty environments, ensure the valve meets safety standards and has an appropriate IP rating.
- Moisture Levels: High moisture levels require materials that resist rust and corrosion, such as brass or stainless steel.
| Environment | Recommended Material | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Harsh Outdoor | Stainless Steel, Brass | UV resistant, durable |
| Corrosive | Stainless Steel, Specific Plastics | High corrosion resistance |
| Explosive/Dusty | Certified Materials (e.g., ATEX) | Safety compliance, IP rated |
| High Moisture | Brass, Stainless Steel | Rust-resistant |
Safety considerations are critical, especially if the valve is used in applications involving human consumption like beverages. Stainless steel is often recommended due to its compliance with safety standards.
For more details on safety and environmental factors, see our article on what is the difference between a 2 way and 3 way solenoid valve?.
By carefully considering these factors, you can ensure that you select the best 2 way solenoid valve for your specific agricultural applications. This will help you achieve optimal performance and longevity for your equipment.
Performance and Maintenance of Solenoid Valves
Response Time and IP Rating
Understanding the performance metrics of solenoid valves, especially the 2 way solenoid valve, is crucial for ensuring optimal operation in agricultural applications. Two key performance indicators to consider are the response time and the IP rating.
Response Time
The response time of a solenoid valve is the interval between the activation of the solenoid and the point at which the pressure has fallen to 10% or risen to 90% of the maximum test pressure. This metric is influenced by several factors, including the construction of the valve, coil properties, atmospheric pressure, and the viscosity of the medium being controlled.
| Valve Type | Response Time |
|---|---|
| Direct Operated Valves | 5 to 50 ms |
| Indirect Operated Valves | 50 to 1500 ms |
Direct operated valves generally have faster response times compared to indirect operated valves. This quick response time is beneficial for applications requiring near-instantaneous switching, such as in crop spraying systems where precise control over fluid flow is essential.
IP Rating
The IP (Ingress Protection) rating of solenoid valve coils indicates the degree of protection against access to hazardous parts, as well as the ingress of water and dust. Most solenoid valve coils, including those from JP Fluid Control, have an IP-65 rating, which provides robust protection against water and dust ingress.
| IP Rating | Protection Level |
|---|---|
| IP-65 | Dust-tight and protected against water jets |
Choosing a solenoid valve with a high IP rating ensures that the valve can withstand harsh environmental conditions, thereby extending its service life and reliability in agricultural settings.
Maintenance Tips for Longevity
To maximize the lifespan and performance of your 2 way solenoid valve, regular maintenance is essential. Below are some practical tips to keep your solenoid valves in optimal condition.
Regular Inspection
- Visual Checks: Regularly inspect the valve for any signs of wear, corrosion, or damage.
- Functional Tests: Periodically test the valve’s operation to ensure it is functioning correctly.
Cleaning
- Debris Removal: Ensure that the valve and its components are free from debris and sediment.
- Lubrication: Apply appropriate lubricants to moving parts to reduce friction and wear.
Electrical Components
- Check Connections: Ensure that all electrical connections are secure and free from corrosion.
- Test Coils: Verify the integrity of the solenoid coils and replace any that are damaged or malfunctioning.
Environmental Considerations
- Protective Measures: Use protective enclosures or covers to shield the valve from extreme weather conditions.
- IP Rating Compliance: Ensure that the valve’s IP rating is suitable for the environmental conditions in which it operates.
For more detailed guides on maintaining solenoid valves and other related topics, check out our articles on how does a 2 way control valve work and what is the difference between a 2 way and 3 way solenoid valve.
By following these maintenance tips, you can ensure that your solenoid valves provide reliable performance and have a long operational life, making them a valuable component in your agricultural operations.